Imagine you’re in the middle of a busy workday or enjoying a movie night, and suddenly the power goes out. Everything stops—your work, your entertainment, and even your safety systems might be affected. Today, even a brief blackout can create a lot of hassle. This guide will explain what an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is, how it works, and the different types available to keep your devices safe and running when the unexpected happens.
Let’s dive in and see how a UPS can be your safety net against sudden power cuts.
What is a UPS?
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is your first line of defense against power problems that could damage your equipment or disrupt your operations. Think of a UPS as a gate that stands between your sensitive electronic equipment and the often unpredictable power from the utility grid. It provides emergency power when your main power source fails, ensuring continuous operation of critical equipment.
Why Uninterrupted Power is Critical
In our increasingly digital world, even a split-second power interruption can have serious consequences. Consider this: a momentary power outage in a data center can lead to corrupted files, lost transactions, and hours of system recovery time. For healthcare facilities, continuous power can be a matter of life and death, keeping vital medical equipment operational. In manufacturing, power interruptions can result in ruined production runs and expensive machinery damage. The cost of downtime in these scenarios often far exceeds the investment in a quality UPS system.
The Three Types of UPS Systems
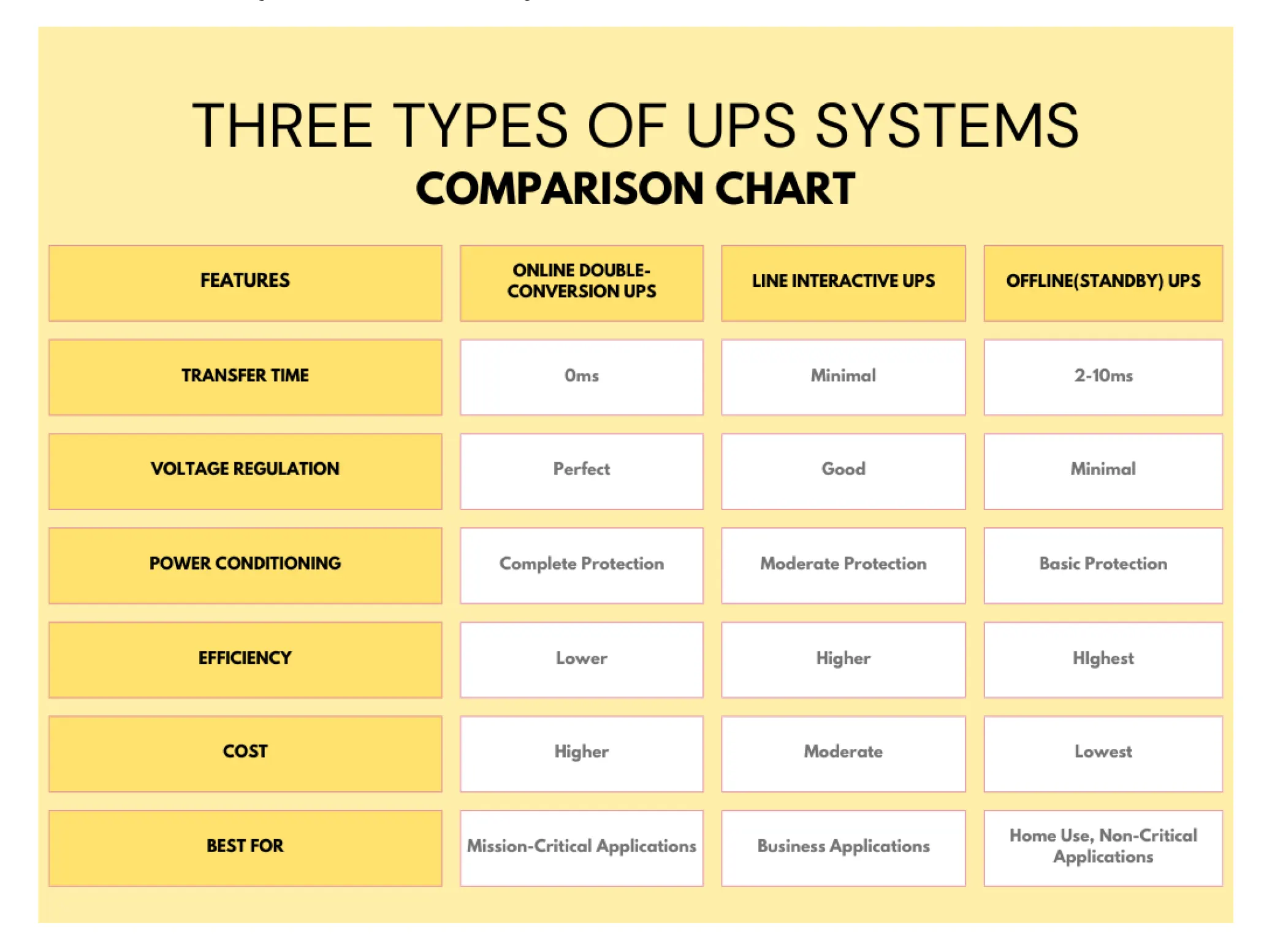
UPS systems protect your valuable equipment from power fluctuations and outages, and they come in three primary types that differ in how they handle electricity:
- The Online double-conversion UPS, Line-interactive UPS, and Offline (standby) UPS. The online double-conversion UPS is like a power purifier—it constantly converts incoming AC power into DC and then back to AC, which means your devices always receive perfectly conditioned power without any interruption; this makes it ideal for mission-critical systems such as data centers or medical equipment, though this level of protection comes at the cost of higher energy consumption and upfront expense.
- The line-interactive UPS strikes a balance by using an internal transformer and automatic voltage regulation to adjust minor power fluctuations on the fly without relying heavily on the battery, making it both efficient and reliable for most office or business environments where power quality is generally stable but occasional surges or sags might occur.
- The offline (standby) UPS offers a simpler, more cost-effective solution by remaining idle until a power outage is detected—then, it switches to battery power, which means there is a brief delay (typically 2-10 milliseconds) and minimal power conditioning; this type is perfect for non-critical applications like home computers or small office equipment where ultra-fine voltage regulation is less important than having a basic backup.
Pros and Cons of Each UPS Systems
1. Online Double-Conversion UPS
The online double-conversion UPS is engineered for environments where power quality is critical. It continuously converts incoming AC power to DC and then back to AC, ensuring that connected devices always receive perfectly conditioned power. This process isolates equipment from all power irregularities, making it ideal for mission-critical operations such as data centers, hospitals, and other sensitive environments.
Pros:
- Zero Transfer Time: Since the conversion process is continuous, there’s no delay when switching to backup power, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Superior Voltage Regulation: Delivers stable and consistent voltage, eliminating risks from surges or sags.
- Complete Isolation: Fully separates your devices from the raw utility power, offering top-notch protection.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: The advanced technology and constant conversion mean a higher upfront investment.
- Lower Efficiency: Continuous conversion can lead to slightly higher energy consumption compared to other types.
2. Line-Interactive UPS
The line-interactive UPS is designed for users who need reliable backup power without the expense of an online system. It uses an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) that adjusts minor fluctuations without switching to battery power immediately. This makes it well-suited for typical office or small business settings where power disturbances are occasional rather than constant.
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable than online UPS systems while still providing strong protection.
- Efficient Operation: Corrects minor voltage issues without draining the battery, thereby extending battery life.
- Balanced Performance: Offers a good compromise between protection and energy efficiency, making it ideal for many commercial and residential applications.
Cons:
- Limited Protection: While it handles common power issues effectively, it may not fully isolate sensitive equipment from all power quality problems.
- Battery Dependence: In severe power disturbances, it will still rely on battery power, which may not offer the instant response required by the most critical systems.
3. Offline (Standby) UPS
The offline or standby UPS is the most basic and economical option, designed primarily for non-critical applications like home computers or small office setups. It remains inactive during normal operations and only kicks in when it detects a complete loss of power, providing a backup to safely shut down systems or keep them running for a short period.
Pros:
- Simplicity: Its basic design makes it easy to use and maintain.
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes very little power during regular operation since it remains on standby until needed.
- Affordability: Typically the least expensive UPS option, making it accessible for budget-conscious users.
Cons:
- Slight Transfer Delay: There is a brief switching delay (usually 2-10 milliseconds) when moving from mains power to battery backup, which might not suit very sensitive equipment.
- Limited Power Conditioning: Offers minimal voltage regulation, meaning it won’t protect against all power quality issues.
Each UPS system caters to different needs:
- The Online Double-Conversion UPS is best for environments where absolute power quality is essential despite its higher cost and energy consumption.
- The Line-Interactive UPS offers a balanced approach for businesses that require dependable protection with improved efficiency and moderate cost.
- The Offline UPS provides a simple, cost-effective solution for home or small office settings where occasional power loss is acceptable, and a brief delay during switching is not critical.
Choosing a Right UPS for Your Needs
When selecting a UPS system, consider these key factors:
- Critical Level of Your Equipment: For mission-critical systems, choose online double-conversion. For standard business equipment, line-interactive works well. For basic home protection, offline UPS is sufficient.
- Power Quality in Your Area: If you experience frequent power issues, consider online or line-interactive UPS systems. In areas with stable power, an offline UPS might suffice.
- Budget Considerations: Balance the initial cost against the potential cost of downtime and equipment damage.
Key Takeaways of Three Types of Uninterrupted Power Supply
Each UPS type serves a specific need:
- Online Double-Conversion UPS is best for environments where absolute power quality is essential
- Line-Interactive UPS offers a balanced approach for businesses requiring dependable protection
- Offline UPS provides a simple, cost-effective solution for home or small office settings
Choose the UPS system that matches your specific needs, considering both your current requirements and potential future growth. Remember, the cost of adequate power protection is almost always less than the cost of downtime or equipment damage. With this guide, you’re now equipped to make an informed decision about which UPS system will best protect your valuable equipment and ensure your operations continue smoothly, even when the power goes out.


